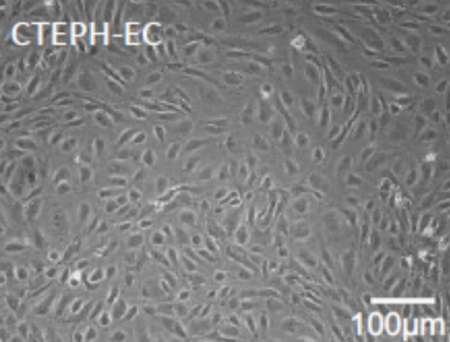
Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension (CTEPH) and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) are two forms of pulmonary hypertension (PH) characterized by obstructive vasculopathy. Endothelial dysfunction along with metabolic changes towards increased glycolysis are important in PAH pathophysiology. Less is known about such abnormalities in endothelial cells (ECs) from CTEPH patients.
The IDIBGI's respiratory diseases research group has published a study that provides a systematic metabolic comparison of ECs derived from CTEPH and PAH patients. The research, led by Dr. Olga Tura, shows that whereas PAH-EC showed significant higher mRNA levels of GLUT1, HK2, LDHA, PDHA1 and GLUD1 metabolic enzymes compared to HPAEC, CTEPH-EC did not. Oxidative phosphorylation associated proteins had an increased expression in PAH-EC compared to CTEPH-EC and HPAE. PAH-EC, CTEPH-EC and HPAEC presented similar HOXD macrovascular gene expression. Metabolic inhibitors showed a dose-dependent reduction in viability in all three groups, predominantly in PAH-EC.
A different metabolic profile is present in CTEPH-EC compared to PAH-EC and suggests differences in molecular mechanisms important in the disease pathology and treatment.
Reference: DOI:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1008061/v1